Guanfacine Side Effects and Warnings
- Brand Names: INTUNIV, TENEX
- Generic Names: guanfacine hydrochloride, guanfacine
- Categories: selective alpha2A-adrenergic receptor agonist
- and ANTI-HYPERTENSIVE
How Guanfacine Works
Guanfacine decreases certain nerve signals from the brain to the blood vessels and the heart. This causes the blood vessels to relax so that blood flows more easily and slows the heart rate. These effects help to lower blood pressure. (4) The drug lowers blood pressure and heart rate, thereby supressing the body's “fight or flight response” by decreasing that activity of part of the brain known as vasomotor center. Many users of guanfacine experience sedation or drowsiness. (5)
INTUNIV can make your child sleepy. One of the most common side effects of INTUNIV is sleepiness.
Used For
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Attention deficit disorder in children ages 6-17
- Oppositional defiant disorder
- Conduct disorder
- Pervasive development disorders
What is the Difference Between Intuniv and Tenex?
Intuniv is extended-release and Tenex is instant-release. Both brands contain the same drug: guanfacine hydrochloride.
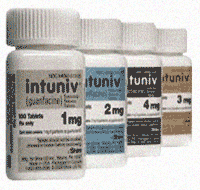
Intuniv Dosage Forms and Strengths
Guanfacine hydrochloride in 1 mg, 2 mg, 3 mg, and 4 mg extended-release tablets.
| Guanfacine hydrochloride | 1 mg | 2 mg | 3 mg | 4 mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color | White/off-white | White/off-white | Green | Green |
| Shape | Round | Caplet | Round | Caplet |
| Debossment (top/bottom) |
503 / 1mg | 503 / 2mg | 503 / 3mg | 503 / 4mg |
Tenex Dosage Forms and Strengths
Guanfacine hydrochloride in 1 mg and 2 mg tablets.
| Guanfacine hydrochloride | 1 mg | 2 mg |
|---|---|---|
| Color | Light pink | Yellow |
| Shape | Diamond-shaped | Diamond-shaped |
| Debossment (top/bottom) |
TENEX / 1 | TENEX / 2 |
Let Your Doctor Know Before Taking This Drug If (2)
- you have or have had serious emotional depression
- you are taking any antidepressant
- you are taking a tricyclic antidepressant
- you are taking any sedative
- you are taking any hypnotic drugs
- you have a circulatory disorder of the brain
- you have angina or coronary heart disease
- you have impaired liver or kidney function
- you are a diabetic
- you have a history of orthostatic hypotension
- you have a very slow heart rate
- you plan to have surgery under general anesthesia in the near future
Like other antihypertensive agents, guanfacine should be used with caution in patients with severe coronary insufficiency, recent myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular disease, or chronic renal or hepatic failure.
Common (Expected) Adverse Side Effects (4)
- Dry mouth (xerostomia) (10-60%)
- Drowsiness and sleepiness (somnolence) (5-39%)
- Sedation (5-30%)
- Headache (0.2-26%)
- Dizziness (2-15%)
- Constipation (2-16%)
- Fatigue (2-15%)
- Abdominal pain (11%)
Less Possible (1-10%) Adverse Effects (4)
If any of the following develop, consult your physician promptly for guidance.
- Hypotension (abnormally low blood pressure) (7%)
- Fatigue and loss of energy (asthenia) (2-7%)
- Impotence (erectile dysfunction) (0-7%)
- Tiredness, sluggishness (lethargy) (6%)
- Dizziness (6%)
- Irritability (6%)
- Nausea (3-6%)
- Decreased appetite (5%)
- Weakness (1-5%)
- Insomnia (inability to obtain adequate or quality sleep) (3-4%)
- Bradycardia (slow heart rate) (3%)
- Palpitations (irregular, hard, or rapid heartbeats) (3%)
- Confusion (3%)
- Depression (3%)
- Dyspnea (difficulty in breathing or shortness of breath) (3%)
- Alopecia (hair loss, baldness) (3%)
- Dermatitis (inflammation of the skin) (3%)
- Diaphoresis (excessive perspiration, sweating) (3%)
- Pruritus (severe itching) (3%)
- Dyspepsia (digestion problems including stomach discomfort or vomiting) (3%)
- Dysphagia (difficulty in swallowing or inability to swallow) (3%)
- Hypokinesia (abnormally slow muscle activity) (3%)
- Leg cramps (3%)
Adverse Effects (Frequency Not Defined) (4)
- Orthostatic hypotension (head rush, dizzy spell)
- Exfoliation
- Rash
- Arthralgia (joint pain)
- Myalgia (muscle pain)
Adverse Effects Reported in Actual Patients (Postmarketing Experience) (4, 5)
- Body as a Whole:
- Asthenia (loss of strength and energy; weakness)
- Chest pain
- Edema (swelling)
- Malaise (feeling of general discomfort, "I just don't feel good.")
- Tremor (shakiness or trembling)
- Cardiovascular:
- Bradycardia (slow heart rate)
- Palpitations (irregular, hard, or rapid heartbeats)
- Syncope (fainting, brief loss of consciousness)
- Tachycardia (rapid heart rate)
- Central Nervous System (CNS):
- Paresthesias (prickly, tingling sensation)
- Vertigo (sensation of irregular or whirling motion, dizziness)
- Eye Disorders:
- Blurred vision
- Gastrointestinal (GI):
- Abdominal pain
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Dyspepsia (digestion problems including stomach discomfort or vomiting)
- Liver and Biliary System:
- Abnormal liver function tests (LFTs)
- Musculoskeletal:
- Arthralgia (joint pain)
- Leg cramps
- Leg pain
- Myalgia (muscle pain)
- Psychiatric:
- Agitation
- Anxiety
- Confusion
- Depression
- Hallucinations
- Insomnia
- Nervousness
- Reproductive System:
- Male: impotence
- Respiratory System:
- Dyspnea (difficulty in breathing or shortness of breath)
- Skin and Appendages:
- Alopecia (hair loss, baldness)
- Dermatitis (inflammation of the skin)
- Exfoliative dermatitis (scaling and itching of the skin, with loss of hair)
- Pruritus (severe itching)
- Rash
- Special Senses:
- Alterations in taste
- Urinary System:
- Nocturia (excessive urination at night)
- Urinary frequency
Rare, serious disorders with no definitive cause and effect relationship to guanfacine have been reported spontaneously and/or in the postmarketing study. These events include acute renal failure, cardiac fibrillation, cerebrovascular accident, congestive heart failure, heart block, and myocardial infarction. (5)
Possible Effects On Sexual Functions (2)
- Decreased libido
- Impotence
DO NOT STOP THIS DRUG SUDDENLY
Sudden withdrawal can produce anxiety, nervousness, tremors, fast or irregular heart beat action, nausea, stomach cramps, vomiting and rebound hypertension.
Withdrawal reactions occur within 2 to 7 days after the last dose. Best to reduce dose gradually (over 3 to 4 days), with periodic monitoring of the blood pressure.
Overdose Side Effects (2)
- Marked drowsiness
- Weakness
- Dry mouth
- Slow pulse
- Low blood pressure
- Vomiting
- Stupor progressing to coma